Ethereum L2 Gas Implementation
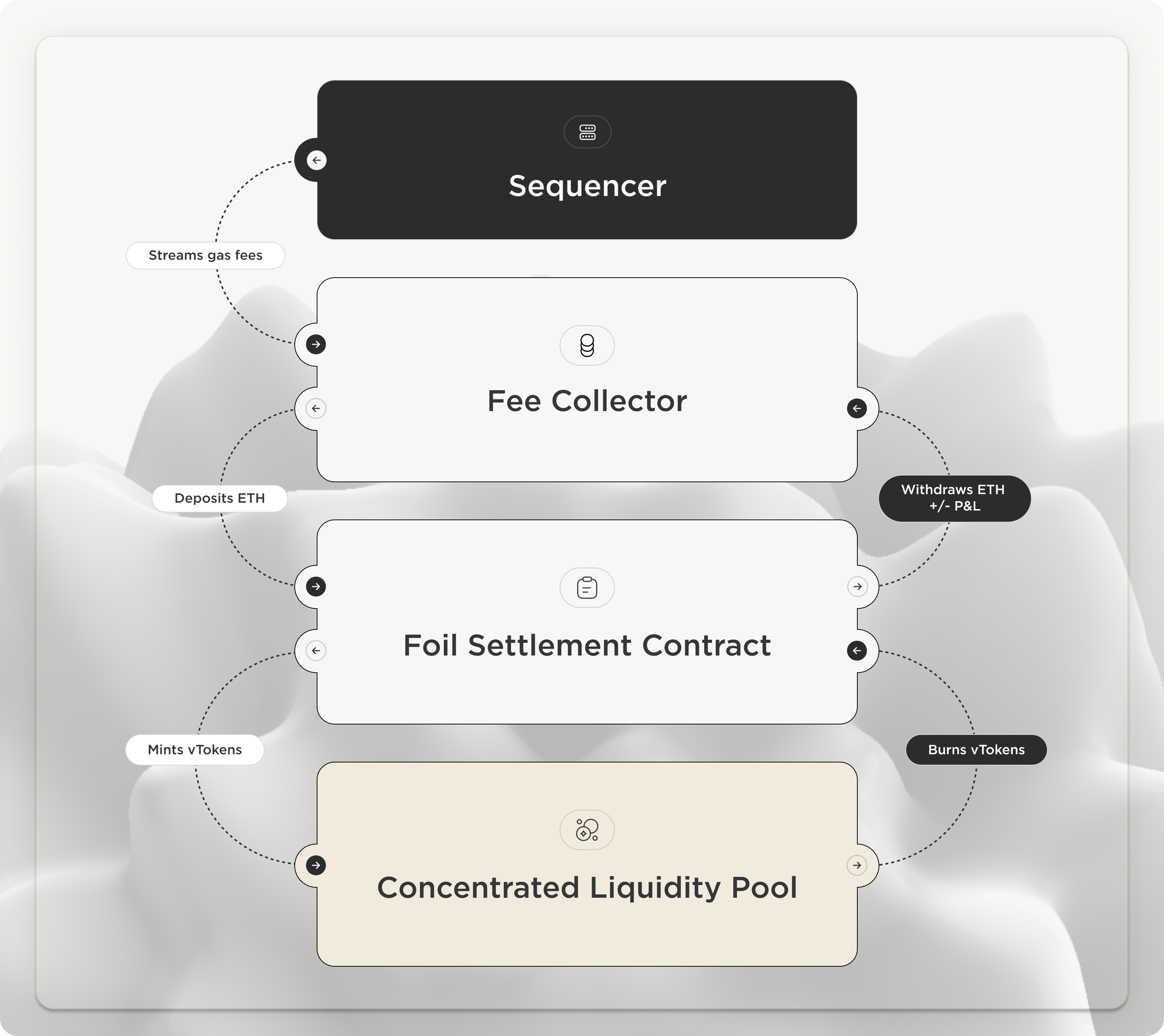
Ethereum L1 gas market liquidity is hard to scale given the cashflow mismatch problem introduced by EIP-1559 (the base fee is the main component of the fee the user wants to hedge). After EIP1559, the base fee gets burnt instead of going to validators, limiting validator revenue to priority tips. This in turn limits validators to sell block production upfront at a liquidity level that doesn’t meet demand.
Rollups with centralized sequencers, as well as Gnosis Chain, have a specific address that earns the totality or a majority of the user fee. Foil can use an NFT issued to the fee collector address, which allows the address to collateralise its positions with future fee revenue. Two different implementations are:
Implementation A:
- Fee Collector Address holds NFT collateral in Foil protocol account
- An automated LP vault LPs a governance-defined range
- There is consistent distributed liquidity of Foil subscriptions for users
Implementation B:
- Fee Collector Address holds NFT collateral in Foil protocol account
- A Safe module is built to enable governance-triggered auctions of Foil subscriptions
- Via governance, large agreements can be settled between the Fee Collector Address and consistent consumers of blockspace in the given L2 or sidechain.
